This document is in slide mode. t to toggle h for help
Understanding and avoiding user induced limit cycles in practical haptic interfaces
William Harwin
w.s.harwin@reading.ac.uk University of Reading. UK and UKAEA (RACE), UKRobotics for human sensorimotor research: basic and clinical, November 2025
Slides at https://www.cybernetia.co.uk/hapticlimitsIntroduction: Haptic realism
Haptics is a bi-directional information channel
- Perceiving the world with exploratory procedures (Lederman and Klatzky, 2009)
- Changing the world with direct interactions (Daniel Wolpert, e.g. puppet master)
Things that enhance haptic realism
- At low frequency (proprioceptive) cues
- weight, mass, constant forces e.g. walls, tables
- At High frequency (vibrotactile) cues
- spatial frequencies across the skin
- Synchronized perceptual cues
- Vision
- Sound
Things that destroy haptic realism
- conflicting cues (visual dominance)
- missing cues (some missing cues are perceived)
Haptel 2008-2012
Haptic system for dental training, work with Kings College, London (dental school and school of education)
- Cue conflict, visually wrong
- Missing cue, sound
- Synchronized cue, sound
The problem of creating the ultimate haptic device
Vibrotactile cues can be vital
- The finger tracking problem
- Follow the edge of a piece of paper (including a corner) with your eyes closed.
- Currently no haptic interface allows that level of proprioceptive and tactile cues
Device related cue conflicts
- Actuator saturation
- Workspace limits
- linkage-linkage and linkage-body collisions
- Device singularities
- Limit cycles
- Excessive energy generation
The lever and types of haptic device
Admittance haptics
Requires a force sensor, ideally at the point of interaction

Impedance haptics (backdrivable)

Relies on the close relationship between the end point force and the joint torques.
Admittance haptics
- more expensive (uncommon)
- higher end-point mass
- frequency range lower
- easier to disperse energy into the mechanism
- actuator push through does not happen
(from 1:11)
The Moog Simodont https://youtu.be/p_iwT8K-wwY is also an admittance controlled haptic interface
Impedance (back drivable) haptics
- Lower cost
- frequency higher
- Smaller workspace (in general)
- Encumbrance in free-space vs stiffness of hard contact
- Materials density, and elasticity Mass of components
To avoid limit cycles follow the energy
Forces involved in a haptic device

Phase portraits
Plot velocity against position
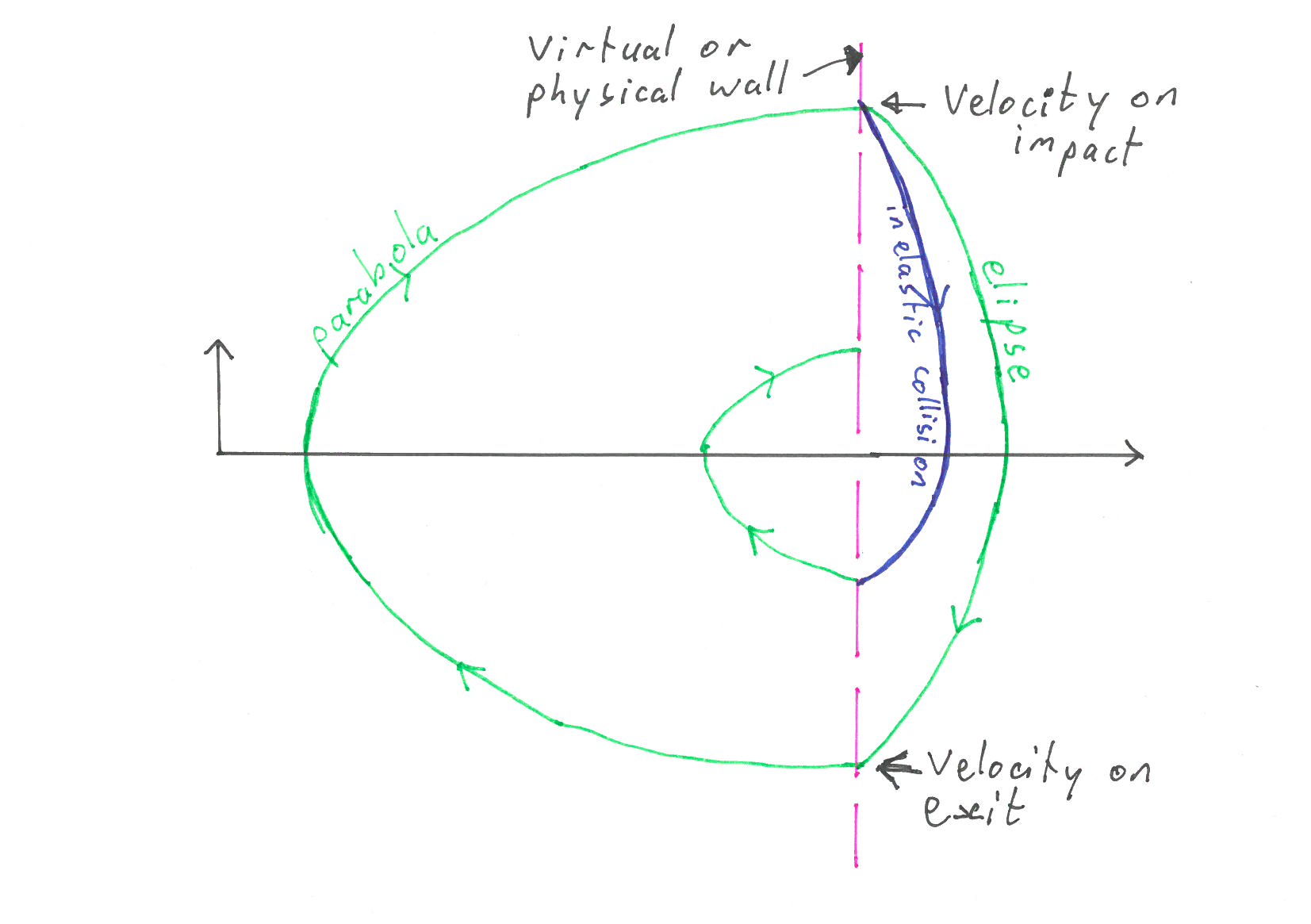
Phase portraits
Plot velocity against position
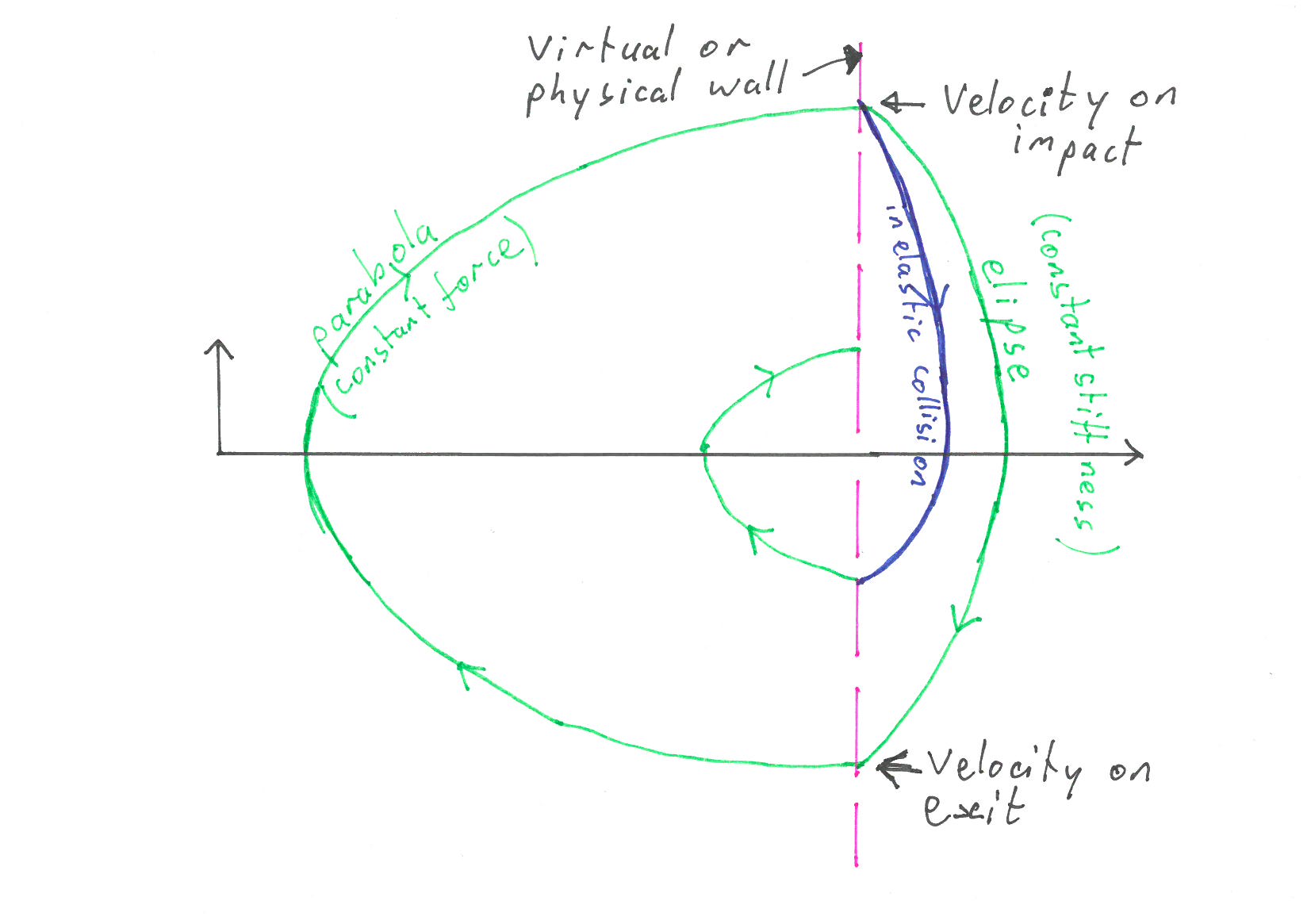
Computational delay
But in any haptic environment there is a delay in computing the actuator forces.
Primary source of delay is the Physics engines
| PBD | Position based dynamics | Physx |
| IBD | Impulse based dynamics | Carbon, Box2D |
| FBD | Force based dynamics | Mujoco, Bullet |
Delay leads to limit cycles
Delay effectively tilts the switching boundary, i.e. the solid contact.

Delay induces secondary vibrations

A librarian solution
Partial solution
- reduce the delay by computing local physics
- provide more ways to loose energy in the machine
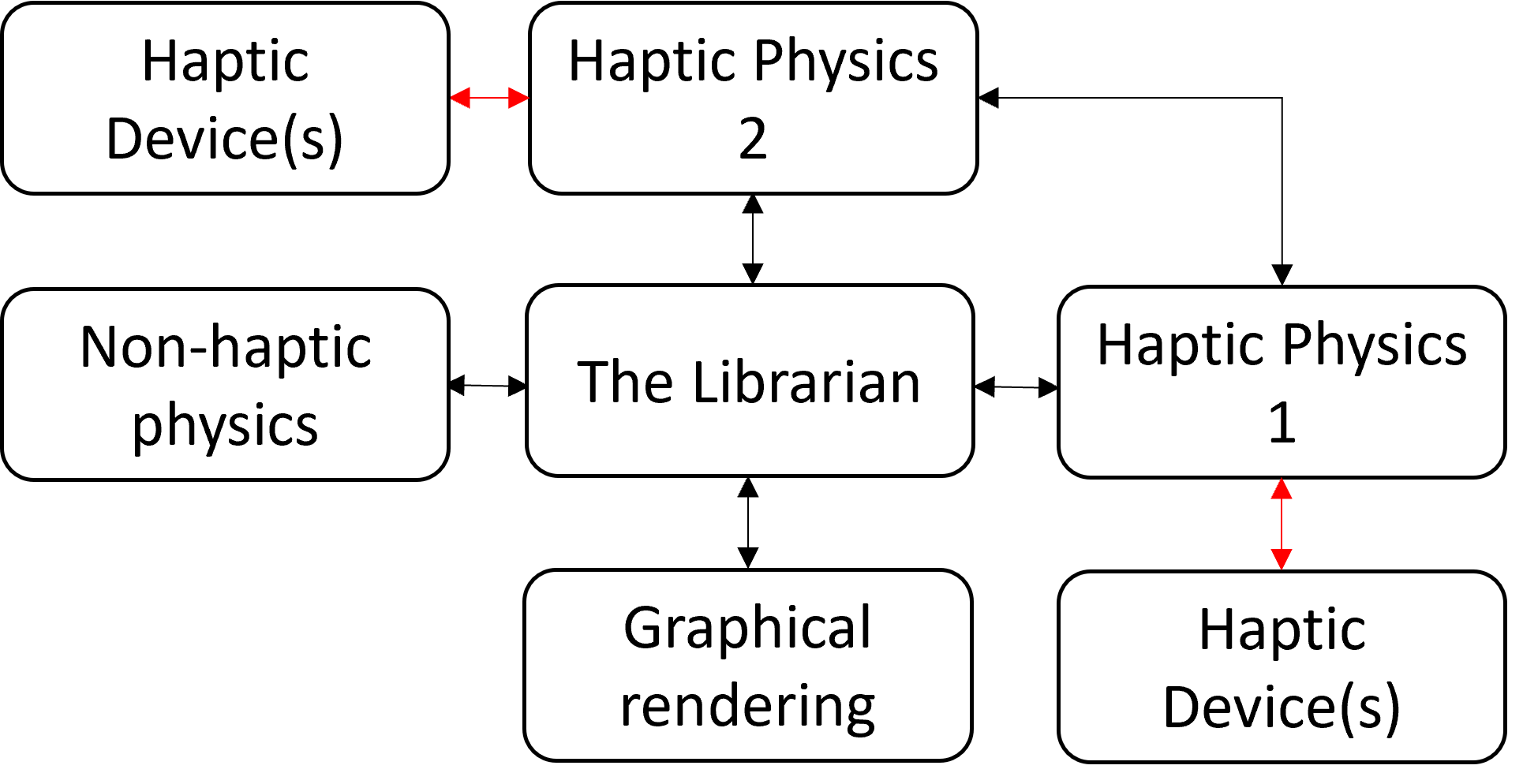
D. Norman et al. "A distributed approach to haptic simulation." TAROS Towards Autonomous Robotic Systems 2022 Springer
Conclusion
- Haptic interfaces can enhance the abilities to interact in a virtual environment
- Haptic illusion can be destroyed in many ways (singularities, actuator saturation, etc)
- Delay leads to instability usually manifested as a limit cycle
- Controlling energy is an important component of maintaining haptic realism
- Haptic interfaces provide an engineering challenge that must consider perception
Additional notes
- https://www.cybernetia.co.uk/hapticlimits
- Haptic-Teleoperation Lecture Series UKAEA
- (https://peterscarfe.com/matrix.html)